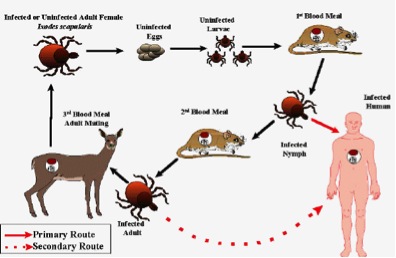
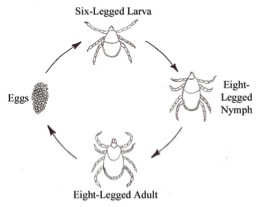
tick life cycle nz
These hatch into larvae. Ticks begin their lives as eggs.

Life Cycle Of Spinose Ear Tick Otobius Megnini Acari Argasidae Infesting The Race Horses In Nuwara Eliya Sri Lanka Sciencedirect
In general the life cycle of a hard tick is as follows.
. In early spring ticks begin to lay their eggs. Ixodidae Argasidae known to occur naturally in the New Zealand subregion is given. However the Ministry is not aware of any cases of.
Hosts geographic distribution and relevant. Life Cycle of Ticks. Egg six-legged larva eight-legged nymph and adult.
Ticks have backwardly pointing teeth Handle your clothing carefully When you come in place your clothing somewhere warm to dry out in a hot room or on a hot windowsill. Depending on the species ticks can live for up to three years during which they go through four distinct life stages. When the egg hatches a six-legged larva emerges.
Lets review the life-cycle of a tick. Ticks locate potential hosts by sensing odor body heat moisture andor vibrations in the environment. The life cycle of a tick can be divided into four sections.
This protozoan Theileria orientalis ikeda is the one currently. The life cycle of ticks Eggs. The majority of hard ticks require three different hosts to complete their development.
Ticks go through four life stages. Ticks have four stages to their lifecycle namely egg larva nymph and adult. Theileria is a protozoan which acts as a parasite spread by the saliva of ticks as they suck the hosts blood.
Ticks typically have three life stages adults which feed on an animal then drop off to lay eggs. Now let us look at their life cycle to get a better understanding. Ticks need energy from blood in order to grow develop and lay eggs.
Since there are so many different tick species the duration of this life cycle varies greatly from a. Most ticks go through four life stages. Without blood ticks cant do any of this.
Its important to be. These eggs are the first of the four distinct life stages that make up the tick life cycle. This nymph can over-winter in quite cold temperatures.
Larvae nymph adult and egg. The life cycle of a tick is completed after four stages namely egg larva nymph and adult it requires more than a year to complete a full life cycle. However they can lay eggs just.
1 The Egg Stage 1 After the adult female tick has acquired a proper blood meal she mates with the. Ticks are a clear illustration of how food works as an energy source. Ixodes scapularis the black-legged deer tick which is the primary vector for Lyme disease has a four-stage life cycle and a lifespan of about two years.
A nymph seeks out and feeds on a. It is called a three-host tick with each of its growing stages - larvae nymph and. After hatching from the eggs ticks must eat blood at each stage in order to move on to.
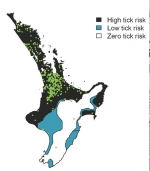
Ticks have the potential to pose public health and biosecurity risks because they can carry and transmit human and animal diseases. Stages in the Life Cycle of Ticks. These stages are egg larvae or seed tick nymph and adult.
Ticks need energy from blood in order to grow develop and lay eggs. Generally adult female hard ticks breed while on the host animal and then drop to the ground to lay eggs. In spring the nymphs now 2-3mm attach to another host and engorge again over three to five days expanding to about 5mm.
The ticks will dry out. A newly hatched six-legged larva feeds on a host drops off to the ground and moults to a nymph. New Zealand appears to be lucky in having only one major stock tick.
Aside from its missing set of legs the larva looks a lot like an adult tick. After hatching from the eggs ticks must eat blood at every stage to survive. A tick begins its life as an egg.
A list of all the species of ticks Acari. Ticks are not able to lay eggs directly on a host they must first detach. Without blood ticks cant do any of.
Once the egg hatches a tick needs a blood meal at each stage in order to survive and continue to grow. Egg larva nymph and adult. If you have poorly-drained pasture.
Ticks are a clear illustration of how food works as an energy source. Tick season has various peaks corresponding to the life-cycle but generally numbers are higher during the warmer months and they tend to over-winter in New Zealand when they are less. During this development ticks go through four stages of life.
There are many different species of tick in the world but Hlongicornis is the only one found in New Zealand. Ticks can live without a blood meal for over a year so leaving pasture un-grazed and hoping the ticks will die from lack of food isnt a very practical option. Egg larva nymph adult.
Hardy Ticks Well Equipped To Survive Thrive

Life Cycle Of A Multi Host Argasid Tick Example Is Ornithodoros Download Scientific Diagram

Three Host Life Cycle Of Ixodes Derived From Ref 13 Download Scientific Diagram
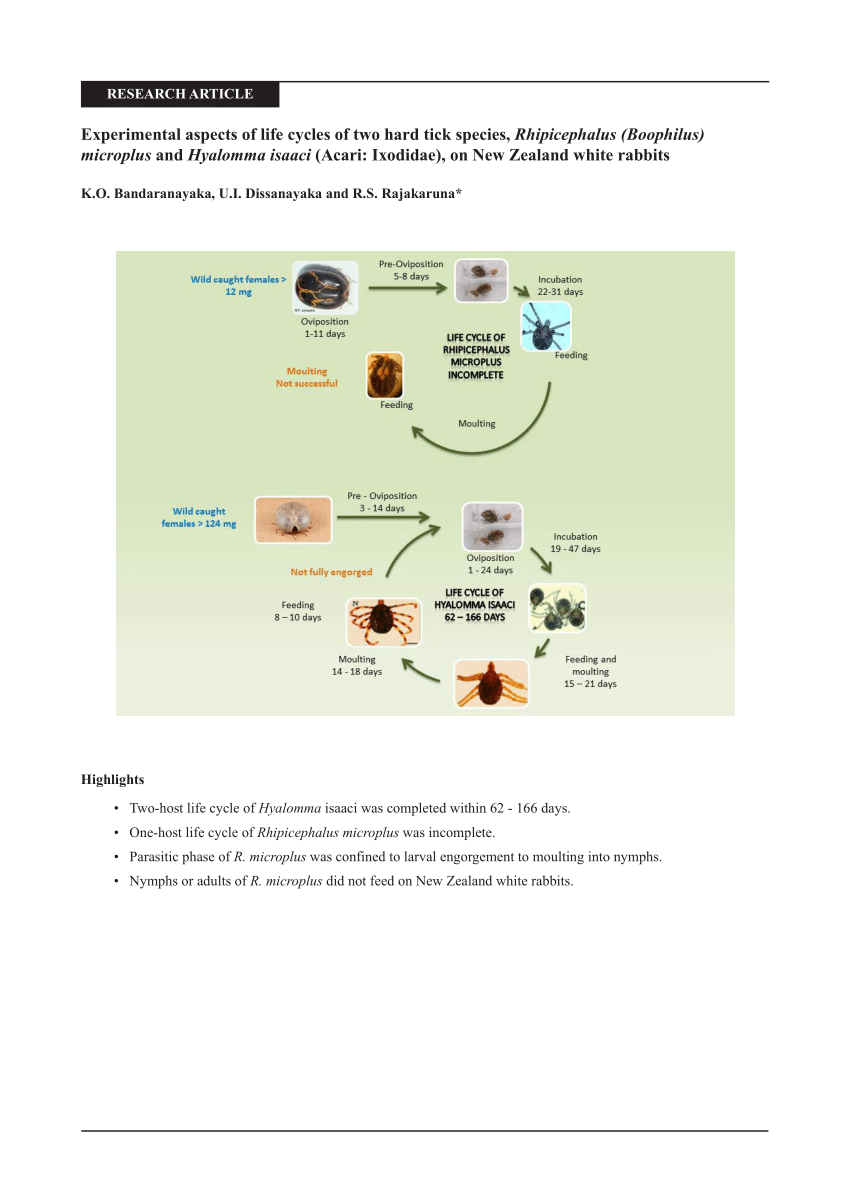
Pdf Experimental Aspects Of Life Cycles Of Two Hard Tick Species Rhipicephalus Boophilus And Hyalomma Isaaci Acari Ixodidae On New Zealand White Rabbits

Life Cycle Of Theileria Parva In Cattle And The Ixodid Tick Vector Download Scientific Diagram
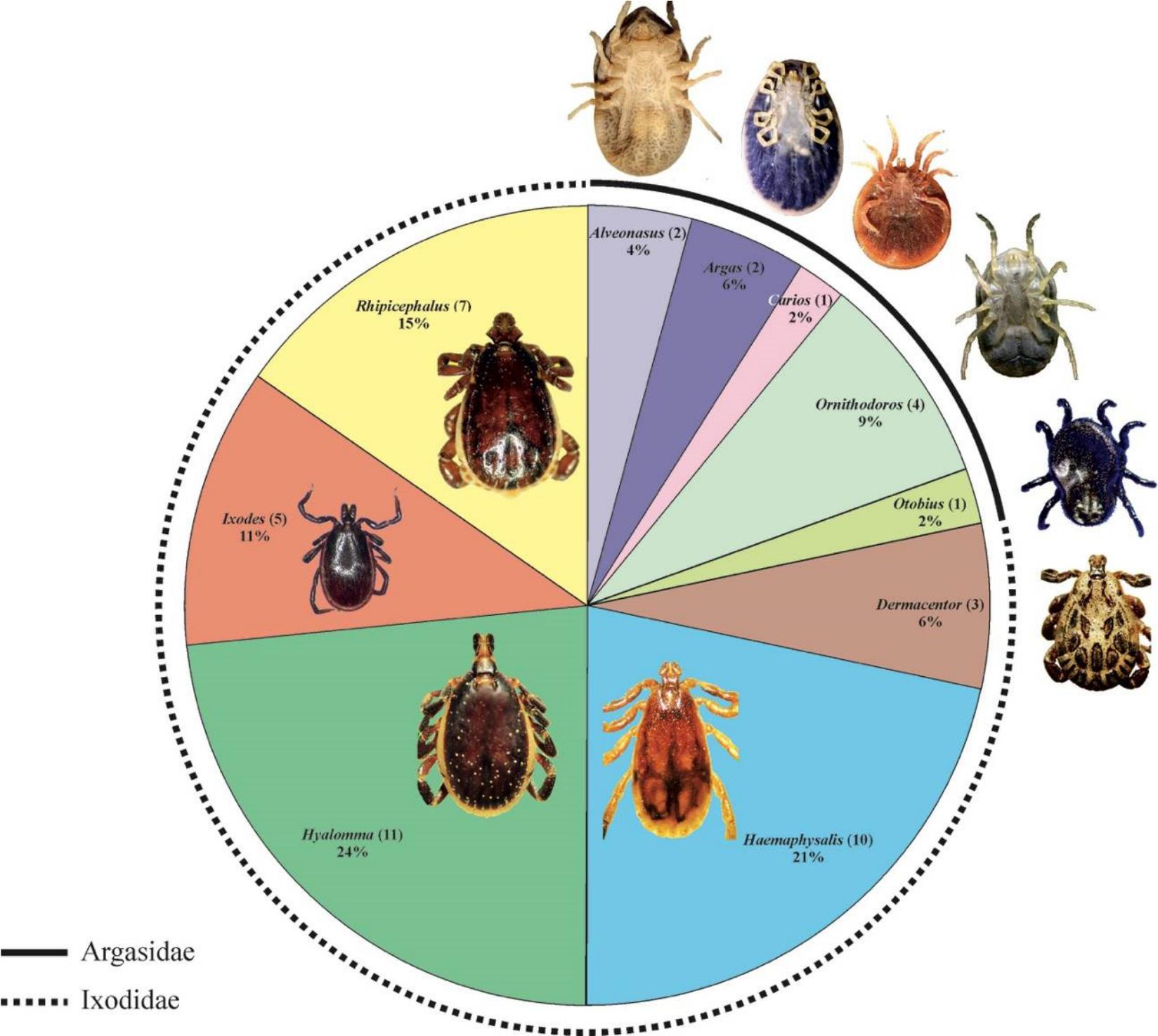
The Updated List Of Ticks Acari Ixodidae Argasidae Occurring In Iran With A Key To The Identification Of Species

Ticks Found On Canterbury Dogs Stuff Co Nz
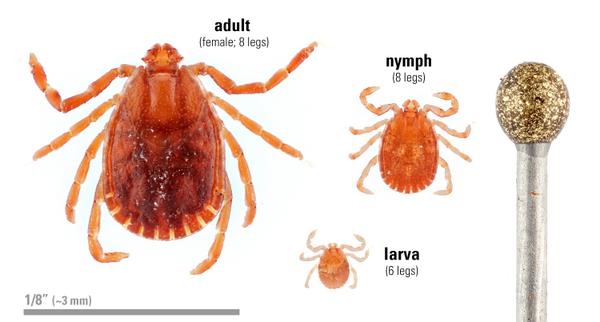
Asian Longhorned Tick Nc State Extension Publications

Life Cycle Of The Ixodes Tick Vectors Of Lyme Borreliosis Reservoir Download Scientific Diagram